elbow flexion compression test|ulnar nerve entrapment at elbow : purchaser Elbow Flexion Test is a neurological dysfunction test used to determine the cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar nerve ). Technique. Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step2. Ask the patient to actively fully elbow flexion with wrist extension and 90 degree shoulder gridle . Encontre a CAIXA; Fale Conosco; . Basta fazer a atualização cadastral no app “CAIXA Tem” e informar sua ocupação (ramo de atuação/trabalho), seu rendimento (renda declarada) e, após a análise de crédito, solicitar o empréstimo via “CAIXA Tem”. . Se você é MEI, as parcelas do seu empréstimo serão debitadas todo mês na .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webMirian Gabriela OFICIAL. @eymirian01. ·. Aug 30, 2021. GRUPO PRIVADO APENAS HOJE 19,99 REAIS MEUS AMORES ️ ♥️ PROMOÇÃO ♥️ PIX 18997995766 CEL , .
Elbow Flexion Test is a neurological dysfunction test used to determine the cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar nerve ). Technique. Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step2. Ask the patient to actively fully elbow flexion with wrist extension and 90 degree shoulder gridle .Elbow Flexion Test. Typically performed bilaterally with the shoulder in full .
Combined pressure and flexion test: a combination of the above two tests; . Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve caused by anatomic compression in the medial elbow. Diagnosis is made clinically with presence of sensory changes to the ring and little finger, intrinsic .Purpose. Evaluate Cubital Tunnel and Ulnar Nerve as a cause of elbow pain. Description. Patient is seated or standing. Arm is abducted. Patient holds elbow in maximal flexion while examiner holds pressure at the cubital tunnel. Hold for .
The Elbow Flexion Test is a neurological test to assess the presence of cubital tunnel syndrome, a common entrapment neuropathy. resisted elbow flexion with forearm supination (compression at bicipital aponeurosis)
Elbow Flexion Test. Typically performed bilaterally with the shoulder in full external rotation and the elbow actively held in maximal flexion with wrist extension held for one minute. Symptoms are produced as maximal elbow .
The elbow flexion test for cubital tunnel syndrome draws the aponeurosis of the flexor carpi ulnaris taught over the ulnar nerve which may elicit symptoms of.Combined pressure and flexion test: a combination of the above two tests; apply pressure to the ulnar nerve just proximal to the cubital tunnel with the elbow in 20 degrees of flexion; maintain . In the elbow compression–flexion test, the examiner places pressure over the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel while holding the elbow flexed and the wrist in neutral position to prevent creating secondary pressure at the .
The sustained position of elbow flexion can place a stretch on the ulnar nerve due to the position of the nerve relative to the bones, which reproduces the symptoms of ulnar nerve compression. In some patients, the ulnar nerve .
The elbow flexion test is a little known, inadequately standardized, and poorly understood clinical test for the cubital tunnel syndrome. To evaluate and define this test, 13 patients with clinical and electrophysiologic evidence of cubital tunnel syndrome were tested with elbow flexion in a standardized manner. . Nerve Compression Syndromes .We evaluated the elbow flexion test in 216 elbows without compression of the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel and without other neuropathies. We used Rayan's four positions as our test. The percentage of positive tests was only 3.6% at one minute, whereas evaluating the responses at three minutes w .When the elbow flexion test is positive, there appears to be a correlation with electrophysiologic cirteria for compression at the elbow. Like the Tinel's test, there is a significant false positive incidence of up to 10 percent.; If the patient experiences mild symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome, conservative measures include anti-inflammatory medications and elbow pads.The Elbow Flexion Test is a physical examination test that is used to evaluate the presence of cubital tunnel syndrome, which is a compression of the ulnar nerve as it passes through the cubital tunnel at the elbow. Here is the procedure for performing the Elbow Flexion Test:
Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow is called cubital tunnel syndrome. Numbness and tingling in the pinky and ring fingers are common symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome. . The test sends an electric current down the arm and looks to see if the current gets slowed along its path. If the current gets slowed down, this is likely an area of .
The elbow flexion test also assesses the ectopic activity of sensory axons and the specific test position has been described in a variety of ways. . Median nerve compression test in carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis reproduces signs and symptoms in affected wrist. Orthop Rev. 1985; 14:41-45. Google Scholar. 31. Presentation varies based on location of compression within Guyon's canal and may be. pure motor. pure sensory. mixed motor and sensory. Symptoms. pain and paresthesias in ulnar 1-1/2 digits. . positive elbow flexion test. Diagnosis. Clinical and EMG/NCS. diagnosis confirmed with history, physical exam and EMG/NCS . They found the following sensitivities for 4 provocative tests: 0.70 for Tinel sign, 0.32 for elbow flexion, 0.55 for pressure provocation, and 0.91 for the elbow flexion-compression test. 37 A similar study conducted by Beekman et al 38 found the sensitivity and specificity of Tinel sign to be 0.62 and 0.53, respectively.
Clinical test for the physical examination of the upper extremity.
negative test = compression is held for 60 seconds, and the patient has no symptoms; Elbow flexion test: flex the patient's elbow, and apply overpressure (i.e. at maximum passive flexion of the elbow) hold this position for a maximum of 60 seconds, stopping sooner if / when the patient complains of symptoms along the ulnar nerve distribution
For the shoulder internal rotation elbow flexion test position, 90° abduction, maximum internal rotation, and 10° flexion of the shoulder were combined with the elbow flexion test position. The test was considered positive if any symptom for cubital tunnel syndrome developed <5 seconds. . Compression neuritis of the ulnar nerve at the elbow . The Vertical Compression Test and Elbow Flexion Test are taught by the Institute of Physical Art as part of the Functional Manual Therapy Curriculum . References. Collins, CK et al. Reliability and Validity of the Saliba Postural Classification System. J Man Manip Ther. 2016 Jul; 24(3): 174–181. Cubital tunnel syndrome (CubTS) is the second most common peripheral entrapment neuropathy of the upper extremity and is related to repetitive or prolonged elbow flexion. 2,5 The causes of CubTS are suspected to be factors related to structural changes along with dynamic elbow flexion, such as increased extraneural pressure in the cubital tunnel .
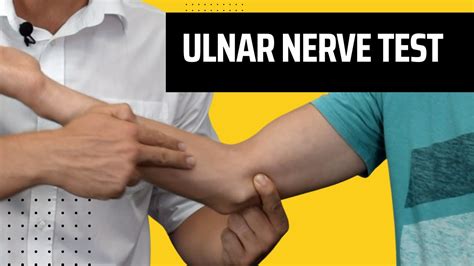
For cubital tunnel syndrome, sensitivities were 69%, 54%, and 46% for the scratch collapse test, Tinel test, and elbow flexion/compression test, respectively. The scratch collapse test had the .Tenderness at the radiocapitellar joint at low flexion angle is markedly diminished at more than 90 degree of flexion with maintaining manual compression force is marked as positive test. Flexion-Pronation plica test [edit | edit source] Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step 2. Patient elbow in extended and forearm pronated . In the elbow compression–flexion test, the examiner places pressure over the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel while holding the elbow flexed and the wrist in neutral position to prevent creating secondary pressure at the carpal tunnel or Guyon canal, which can also cause hand numbness (Figure 18.5). The examiner should also assess for more .
During flexion of the elbow joint, the ulnar nerve gets stretched because of this anatomical position. Repetitive elbow flexion and extension can cause further damage and irritation to the ulnar nerve. . Provocative tests like sustained elbow flexion for one minute or compression of the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel region may also be . Reproduction of symptoms with flexion of the elbow raises a strong suspicion of compression at the level of the elbow in the cubital tunnel. It is important to inquire if the patient notices a "snapping" or "popping" in the elbow, which indicates nerve mobility within the cubital tunnel and indicates ulnar nerve transposition may be appropriate . The elbow flexion test is performed with the patient either sitting or standing. The patient is instructed to maximally flex . stress and axial compression and flexion of the elbow. Figure 15-32 In testing for Tinel’s sign, the patient is seated with the elbow in slight flexion. The examiner grasps and stabilizes the patient’s wrist
ulnar nerve entrapment special tests
UNE may be caused by extrinsic or intrinsic compression or stretch of the ulnar nerve. Common etiologic factors include/prolonged elbow compression on hard surfaces, compression by normal or anomalous anatomic structures, repetitive/prolonged elbow flexion (often during sleep), perioperative positioning, chronic ulnar nerve subluxation, or .
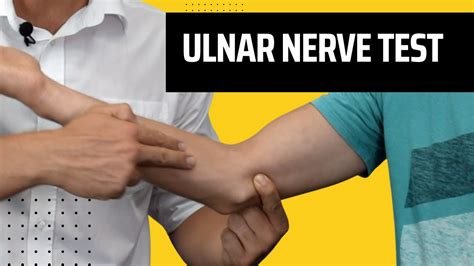
elbow flexion t.: for cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar nerve compression at elbow); the examiner holds the elbow in passive maximal flexion. Tingling in the ring and little finger is positive for ulnar nerve irritation. gravity stress t.: for medial instability; the supine patient has the externally rotated arm out over the edged of the table. With elbow at 20 degrees, the weight of the . This tutorial takes you through this great test that you can use to diagnose your patients with an Ulnar Nerve Entrapment! It teaches you the methodology beh.The elbow flexion test is demonstrated to be a useful, reliable, and provocative test for the cubital tunnel syndrome and supports a locally induced segmental ulnar nerve ischemia as the cause of symptoms. The elbow flexion test is a little known, inadequately standardized, and poorly understood clinical test for the cubital tunnel syndrome. To evaluate and define this .
The direct compression test is executed simply applying direct continuous pressure over the Cubital tunnel. The elbow flexion test is completed by passively flexing the elbow to the maximum angle for 1–3 min. The sensitivity and specificity of these tests do vary in the literature (Table 11.1) [3,4,5]. The clinician should remain cognizant of .
We evaluated the elbow flexion test in 216 elbows without compression of the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel and without other neuropathies. We used Rayan's four positions as our test.
dynisco basic pendulum impact tester versus charpy
pendulum impact charpy tester
webCom a 365Scores você acompanha em tempo real o resultado dos jogos Futebol de hoje em andamento e mais de 1000 competições pelo mundo.
elbow flexion compression test|ulnar nerve entrapment at elbow